Abnormal Movement Clinic and Parkinson’s Disease
Movement disorders are a group of neurological diseases characterized by a decrease, loss or exacerbation of body movements that severely affect the quality of life of patients who suffer from them. There are two classifications of movement disorders: Hypokinetic and Hyperkinetic.
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson’s is a chronic degenerative pathology that manifests itself over time. Worldwide, between 5% and 10% of the population suffers from this disease.
It is characterized by slowness of movement, which may be accompanied by stiffness, tremor, decreased movement and alterations in posture as well as balance, the symptoms appear slowly. In the early stages of Parkinson’s disease, the face may have a slight or no expression. The arms may not swing when you walk. Speech may become soft or incomprehensible.
This disease is related to a decrease in brain chemicals (mainly dopamine) and its treatment is aimed at replacing this substance, and in some cases, optimizing the brain coordination system through brain surgery known as neuromodulation.
At the Neurological Center of Hospital Galenia, we perform a global assessment of the patient with Parkinson’s, we select and perform the surgery, with the most highly qualified personnel.
Parkinson's is a chronic degenerative pathology that manifests itself over time.
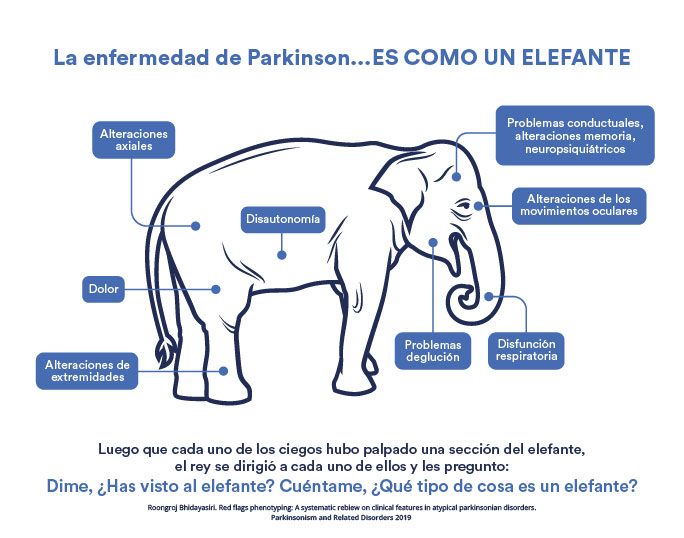
Parkinson’s disease is a huge challenge to understand. When we are blind, each specialty will see the problem in isolation, without understanding that it is a bigger problem. These are the symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. Our strength is Parkinson’s disease. We also treat less frequent movement disorders and rare diseases that produce movement-related disorders. We have advanced therapies available, such as deep brain stimulation surgery and infusion therapies.

Hypokinetic
These are disorders where movements are reduced.
Hyperkinetic
These are disorders where mobility is increased
This is the most common and usually progresses affecting the hands, head and voice, with deterioration in functionality.
People with dystonia have involuntary muscle contractions that can often interfere with everyday functions such as sleeping, walking, eating and speaking. They affect the posture of one or more muscle groups, causing deformities, pain and severe functional impairments that can lead to total disability.
Focal dystonias are often successfully treated using botulinum toxin injections (Botox), while generalized forms can be treated with deep brain stimulation.
These are irregular involuntary movements that affect the limbs, trunk or facial muscles. They may have a genetic origin, as in the case of Huntington’s disease or Wilson’s disease, where several body regions are affected and are associated with early intellectual deterioration; or focal choreas, related to cerebral infarctions or complications of diabetes mellitus.
These typically cause facial movements after exposure to psychiatric or gastrointestinal medications and may affect body image or function.
These are sudden, rapid and short-lasting movements. They are often associated with various diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (in the case of myoclonus) or Tourette syndrome (in the case of tics).


